A systematic method for identifying high potential employees is one of the most crucial components of developing a solid succession plan (AIAHR 2021). In this article, I drill deep into how the 9 box grid is used in performance management to create individualized growth plans and succession planning to identify prospective successors.
One of the most widely used tools in performance management is the 9 box grid. Employees are mapped against two axis: current performance and future potential. Historically, the focus was on leadership, but the grid has been adapted for use with other employees, such as those with specialized abilities that might be vital to an organization.
What is the 9 - Box Grid?
The 9-box grid is a technique for assessing an employees present and potential degree of contribution to the business (Wells 2018). The grids vertical (y) axis represents development potential, which refers to an individuals ability to advance through the ranks in a management or professional role. The meaning of the y-axis can be modified based on the environment and priorities of an organization. The horizontal (x) axis reflects an employees current overall performance, indicating whether the individual is currently performing below, at, or above expectations.
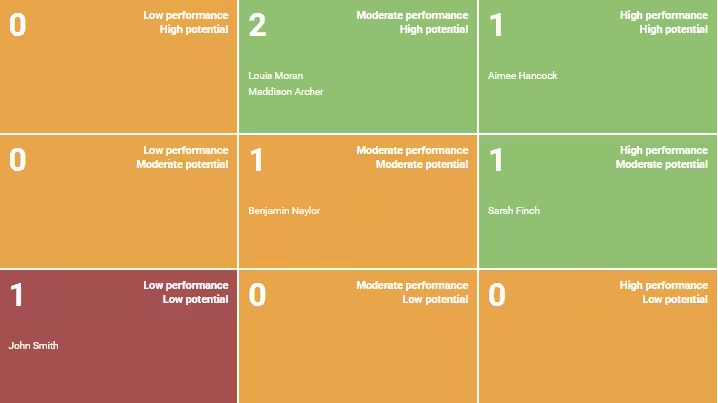
As shown in Table 1 below, individuals in the upper right quadrant are recognized as high-potential candidates for succession when performance and potential are examined and plotted on the graph. Those in the lower-left quadrant may need to be transferred or removed from the company. The potential and performance are then plotted on a 3 x 3 grid, resulting in the nine-box grid. The grids boxes identify areas where more investment is required to develop future leaders.
Table 1: Nine (9) Box Diagram
Creating a 9 Box Grid
Step 1. Assessing Performance
The 9 box grid is divided into three performance levels: low, moderate, and high. Employees are graded on this performance scale during their performance evaluation. The benefit of this approach is that it adheres to the work criteria as established in the organizations employment structure while also relating to the persons goals. Some businesses may have less defined job hierarchies and operate with more personal aims; in this scenario, measuring target achievement might be more critical.
Step 2. Assessing Potential
The potential axis is the other axis of the 9 box grid. During the performance review, potential should also be rated, and it frequently falls into the following categories.
- Low potential | working at full potential. An employee is working at full potential and is unlikely to improve, either because they are at maximum capacity or lack motivation.
- Moderate potential | develop in current role. Employees in this quadrant have the potential to further develop within their current role. This can be in terms of performance and proficiency.
- High potential | eligible for a promotion. An employee is eligible for promotion, either immediately or within two to three years.
Step 3: Putting it all together
The following step is to plot performance and potential on a 3 x 3 grid, yielding the 9 box grid. The intersection of the two will assist evaluate the employees present position and any necessary intervention. The models most important benefit is the talent management advice it delivers for each of the grids 9 Boxes.
Using the 9-Box Grid for Performance Management
After categorizing employees into the nine quadrants, supervisors may construct unique development plans for each person depending on their categorization. In general, you want to invest the most time, effort, and resources in high-potential individuals and the least in low-potential performers. Investment efforts should rise as you travel farther right and higher on the matrix, and decrease as you move further left and below.
Individuals who have been recognized as poor achievers with low potential usually require immediate treatment. It is critical to determine the source of the problem, which might be a lack of fit with the position, ambiguous role expectations, or a poor onboarding experience. You dont want to over-invest in these people in the long run, but its crucial to see whether you can do anything to help them become better performers over time.
The Limitations of the 9-Box Talent Grid
The main difficulty with adopting the framework is that it is vulnerable to some degree of subjectivity and human error if scientific assessment tools are not used. Managers perceptions might be subjective, twisted, or erroneous due to misunderstanding or personal prejudice. We all come from various backgrounds and have distinct perspectives that impact our judgments, especially when dealing with people.
There is a concern that categorizing employees encourages employee labeling, which may be challenging to unstick, and that managers use these labels as shortcuts when addressing personnel. For example, if an employee is allocated to the bottom left corner of the grid, they have deemed a weak employee and may find it challenging to overcome this classification. The 9 box diagram is only effective if managers discuss and define how they will measure potential and also use the grid fluidly so that employees do not get permanently branded.
Aside from the constraints mentioned above, it should be emphasized that the 9-box grid handles just one element in the succession planning process — nominating successors. If it is utilized for succession, it should not account for the complete planning process. For example, before choosing persons as prospective successors, it is vital to identify crucial jobs for which succession planning must be emphasized. Once important positions have been determined, persons in those roles should describe which behaviors and competencies are required for success in that function.
The 9 box grid can be a useful tool to manage all the employees in an organization. As such, it can be used for performance management, talent management, and succession planning. Leaders should focus on nurturing top talent to prepare them for future responsibilities while utilizing the 9-box grid for succession. This may be accomplished through leadership development, coaching, mentoring, and continuous 360-degree feedback. Moderate performers with moderate potential are also likely to play an essential role in a companys succession planning. These employees, in particular, can assist in filling roles left vacant by top talent as they advance. Individuals with intermediate performance and great potential may become candidates for succession if no top talent is available or fit for certain essential tasks.
Carl Tapi is a Consultant at Industrial Psychology Consultants (Pvt) Ltd, a managеmеnt and human rеsourcеs consulting firm. https://www.linkеdin.com/in/carl-tapi-45776482/ Phonе +263 (242) 481946-48/481950 or cеll numbеr +263 772 469 680 or еmail: carl@ipcconsultants.com or visit our wеbsitе at www.ipcconsultants.com